SQL Downloader
SQL Downloader is a component of the data preparation and distribution pipeline (see Data Preparation and Distribution Pipeline). SQL Downloader downloads data from a database endpoint:
- MySQL
- MsSQL
- PostgreSQL
- ADS
Configuration File
Creating and setting up the brick’s configuration file is the third phase of building your data pipeline. For more information, see Phases of Building the Data Pipeline.
For more information about configuring a brick, see Configure a Brick.
Minimum Layout of the Configuration File
The following JSON sample is the minimum layout of the configuration file that SQL Downloader can use. If you are using more bricks, you can reuse some sections of this configuration file for other bricks. For example, the ‘downloaders’ section can list more downloaders, and the ‘integrators’ and ‘ads_storage’ sections can be reused by other downloaders and executors (see Configure a Brick).
This sample describes the use case of one instance of SQL Downloader that downloads two tables from an SQL database.
Copy the sample and replace the placeholders with your values.
You can later enrich the sample with more parameters depending on your business and technical requirements (see Customize the Configuration File).
{
"entities": {
"table_1_name": {
"global": {
"custom": {
"hub": ["column_1_name","column_2_name","column_3_name"]
}
}
},
"table_2_name": {
"global": {
"custom": {
"hub": ["column_1_name","column_2_name","column_3_name"]
}
}
}
},
"downloaders": {
"sql_downloader_id": {
"type": "sql",
"entities": ["table_1_name","table_2_name"]
}
},
"sql": {
"type": "database_type",
"options": {
"connection": {
"server": "server_address",
"database": "database_name",
"username": "user_name"
}
}
},
"integrators": {
"ads_integrator_id": {
"type": "ads_storage"
}
},
"ads_storage": {
"instance_id": "data_warehouse_instance_id",
"username": "dw_email@address.com",
"options": {}
}
}
The placeholders to replace with your values:
| Name | Type | Mandatory? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entities -> table_x_name | string | yes | n/a | The database tables into which SQL Downloader downloads the data |
| entities -> table_x_name -> global -> custom -> hub | array | yes | n/a | The table columns to generate a primary key |
| downloaders -> sql_downloader_id | string | yes | n/a | The ID of the SQL Downloader instance Example: sql_downloader_1 |
| downloaders -> sql_downloader_id -> entities | array | yes | n/a | The database tables into which SQL Downloader downloads the data Must be the same as the database table names in 'entities -> table_x_name' |
| sql -> type | string | yes | n/a | The type of the database Available options:
|
| sql -> options -> connection -> server | string | yes | n/a | The address of the source database server |
| sql -> options -> connection -> database | string | yes | n/a | The name of the source database |
| sql -> options -> connection -> username | string | yes | n/a | The name of the user who has sufficient access rights to the source database |
| integrators -> ads_integrator_id | string | yes | n/a | The ID of the ADS Integrator instance Example: ads_integrator_1 |
| ads_storage -> instance_id | string | yes | n/a | The ID of the Agile Data Warehousing Service (ADS) instance into which the data is uploaded |
ads_storage -> username | string | yes | n/a | The access username to the Agile Data Warehousing Service (ADS) instance into which the data is uploaded |
Customize the Configuration File
You can change default values of the parameters and set up additional parameters.
Download data from an ADS instance
To download data from an ADS instance, set the ‘type’ parameter to ‘Ads’, and specify ADS parameters under ‘sql’ -> ‘options’ -> ‘connection’.
"sql": {
"type": "Ads",
"options": {
"connection": {
"server": "server_address", // optional
"instance_id": "data_warehouse_instance_id",
"username": "dw_email@address.com"
}
}
}
| Name | Type | Mandatory? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| server | string | no | secure.gooddata.com | The URL used to access the ADS instance |
| instance_id | string | yes | n/a | The ID of the ADS instance from which the data is uploaded |
| username | string | yes | n/a | The access username to the ADS instance from which the data is uploaded |
Specify additional load options for the entities
For each entity, you can set up additional load options.
"entities": {
"table_1_name": {
"global": {
"custom": {
"hub": ["column_1_name","column_2_name","column_3_name"],
"query": "custom_query", // optional
"fields": [{"name": "source_field_name", "type": "field_type", "ads_name": "data_warehouse_field_name"}] // optional
}
}
}
}
| Name | Type | Mandatory? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| query | string | no | n/a | A custom query for downloading data When using a schema, replace the schema name with Example: |
| fields | array | no | n/a | The specification of the fields on the ADS instance Format: Example: The following configuration specifies that the 'VehicleID' field in the source database should be the 'id' field in ADS with a type of 'integer'. |
Use incremental load mode
By default, SQL Downloader runs in full load mode. You can choose to change it and use incremental mode when only data after a certain point in time is loaded.
To switch to incremental mode, do the following:
Under ‘sql’ -> ‘options’:
- Add the ‘full’ parameter and set it to ‘false’.
- Add the ‘default_start_date’ parameter and set it to the date that is going to be the initial time from which SQL Downloader will download your data. The date must be in the following format:
"2010-01-01"
"sql": { "type": "database_type", "options": { "full": false, "default_start_date": "2010-01-01", "connection": { "server": "server_address", "database": "database_name", "username": "user_name" } } }Under ‘entities’ -> table_x_name -> ‘global’ -> ‘custom’, add the ‘timestamp_field’ parameter and set it to the name of the column with the timestamp in your data. The referenced column must contain a date.
"entities": { "table_1_name": { "global": { "custom": { "hub": ["column_1_name","column_2_name","column_3_name"], "timestamp_field": "column_name" } } } }
How SQL Downloader runs in incremental mode:
- First run: SQL Downloader loads only the data that has the value in the timestamp column (set in the ‘timestamp_field’ parameter) greater than the initial time (set in the ‘default_start_date’ parameter).
- Second and subsequent runs: SQL Downloader loads the data starting from the greatest value of the ‘timestamp_field’ parameter in the previously loaded data.
If last time data was loaded in full mode, SQL Downloader will use the time of the last successful run as the time to start loading data with.
| Name | Type | Mandatory? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| full | Boolean | no | true | Specifies load mode
|
| default_start_date | string | no | 2010-01-01 | The date that will be set as the start date during the first run of SQL Downloader in incremental load mode |
| timestamp_field | string | no | n/a | The name of the column that will be used as a timestamp for incremental downloads from the database NOTE: The referenced column must contain a date. |
Set partial full load mode for the entities
You can specify partial full load mode for some or all entities. In partial full load, the rows that should be removed must contain the same value in the specified field as the new data does.
[Example]{.ul}: You have two clients: Client A and Client B. You already have data for those clients in your ADS instance from previous data loads. The data for both Client A and Client B is stored in the same table. The table contains, among others, the ‘id’ and ‘client’ columns. The names of these columns are specified in the ‘hub’ parameter of your configuration file (see Minimum Layout of the Configuration File).
This is how your data currently looks in the table on the ADS instance:
| id | text | client |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | aaabbbb | clientA |
| 1 | ccddd | clientB |
Now, you want to reload data for Client A without affecting Client B’s data in the same table.
This is the new data that you want to load for Client A:
| id | text | client |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | eeeeeff | clientA |
After the data load completes, you want the table with the data to look like the following:
| id | text | client |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | eeeeeff | clientA |
| 1 | ccddd | clientB |
Notice that Client A has a different ID and text, and Client B’s data remains the same.
To achieve this output, use partial full load. Set the ‘client’ field to be the partial full load field:
"partial_full_load_field": "client"
After the next data load runs, the table with the data will be updated to look exactly as you want it to.
For comparison, this is what your data would look like if you ran the data load in full load mode:
| id | text | client |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | eeeeeff | clientA |
Notice that the data for Client A is loaded correctly, but the data for Client B is no longer present in the table.
Depending on whether the field that you want to use as the partial full load field does or does not exist in your data, choose one of the following scenarios to set partial full load mode.
[Scenario 1]{.ul}: The field that you want to be the partial full load field [exists]{.ul} in your data
Set up the partial full load field:
If you want to use partial full load for a specific entity, add the ‘partial_full_load_field’ parameter to the ‘custom’ section for the entity and set it to the name of the field that will be used as the partial full load field:
"entities": { "table_1_name": { "global": { "custom": { "hub": ["column_1_name","column_2_name","column_3_name"], "partial_full_load_field": "your_field_name" } } } }If you want to use partial full load for all entities, add the ‘partial_full_load_field’ parameter to the ‘options’ section of the SQL Downloader instance, and set it to the name of the field that will be used as the partial full load field:
"sql": { "type": "database_type", "options": { "partial_full_load_field": "your_field_name", "connection": { "server": "server_address", "database": "database_name", "username": "user_name" } } }
[Scenario 2]{.ul}: The field that you want to be the partial full load field [does not exist]{.ul} in your data
- Choose the field that will be used as the partial full load field.
- Depending on whether you want to use partial full load for a specific entity or all entities, do one of the following:
If you want to use partial full load for a specific entity, configure the ‘custom’ section for the entity.
Add the ‘partial_full_load_field’ parameter, and set it to the partial full load field.
Add the ‘computed_fields’ section so that the partial full load field gets added to your source and stage tables.
"entities": { "table_1_name": { "global": { "custom": { "hub": ["column_1_name","column_2_name","column_3_name"], "partial_full_load_field": "your_field_name", "computed_fields": [ <computed_fields_content_json> ] } } } }The contents of the ‘computed_fields’ section depends on what field you chose to be the partial full load field. For more information about the computed fields and their structure, see Computed Fields. For example, you have multiple clients. Your database contains a separate schema for each client, and the clients are uniquely identified by the ‘client_id’ field in the tables. In this case, the computed field may look like the following:
"computed_fields": [ { "name": "client_id", "type": "string-255", "function": "runtime_metadata|schema", "table_type": ["src"], "key": true, "position": "first", "encoding": "RLE" }, { "name": "client_id", "type": "string-255", "function": "value|client_id", "table_type": ["stg"], "key": true, "position": "first", "encoding": "RLE" } ]If you want to use partial full load for all entities, do the following:
Add the ‘partial_full_load_field’ parameter to the ‘options’ section of the SQL Downloader instance, and set it to the partial full load field:
"sql": { "type": "database_type", "options": { "partial_full_load_field": "your_field_name", "connection": { "server": "server_address", "database": "database_name", "username": "user_name" } } }Add the ‘computed_fields’ section to the ‘ads_storage’ section so that the partial full load field gets added to your source and stage tables.
"ads_storage": { "instance_id": "data_warehouse_instance_id", "username": "dw_email@address.com", "options": {}, "computed_fields": [ <computed_fields_content_json> ] }The contents of the ‘computed_fields’ section depends on what field you chose to be the partial full load field. For more information about the computed fields and their structure, see Computed Fields. For example, you have multiple clients. Your database contains a separate schema for each client, and the clients are uniquely identified by the ‘client_id’ field in the tables. In this case, the computed field may look like the following:
"computed_fields": [ { "name": "client_id", "type": "string-255", "function": "runtime_metadata|schema", "table_type": ["src"], "key": true, "position": "first", "encoding": "RLE" }, { "name": "client_id", "type": "string-255", "function": "value|client_id", "table_type": ["stg"], "key": true, "position": "first", "encoding": "RLE" } ]
Customize the database connection
Depending on your business and technical requirements, you can set one or more optional parameters for your database connection.
"sql": {
"type": "database_type",
"options": {
"connection": {
"server": "server_address",
"database": "database_name",
"username": "user_name",
"fetch_size": number_of_rows, // optional
"connection_validation_timeout": number_of_seconds, // optional
"use_ssl": true|false, // optional
"ssl_mode": "tls_connection_mode" // optional; only when use_ssl=true
}
}
}
| Name | Type | Mandatory? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fetch_size | integer | no | 50000 (for PostgreSQL) n/a (for others) | The number of rows that should be fetched from the database when more rows are needed NOTE: Setting this parameter to a small value (for example, 50) may impact performance. |
| connection_validation_timeout | integer | no | 3600 | The period (in seconds) between the connection check-in and an attempt to validate the connection when checking it out from the pool |
| use_ssl | Boolean | no | false | (For PostgreSQL only) Specifies whether a TLS connection to the PostgreSQL database is enabled.
|
| ssl_mode | string | no | prefer | (Only when 'use_ssl' is set to 'true') Mode in which the TLS connection to the PostgreSQL database runs Available options:
|
Specify additional load options
You can set up additional load options for SQL Downloader.
"sql": {
"type": "database_type",
"options": {
"number_of_schemas_threads": number_of_threads, // optional
"connection": {
"server": "server_address",
"database": "database_name",
"username": "user_name"
}
}
}
| Name | Type | Mandatory? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| number_of_schemas_threads | integer | no | 1 | The number of schemas to download in parallel for one entity |
Add multiple instances of SQL Downloader
When you use only one instance of SQL Downloader, it reads its remote location parameters from the ‘sql’ section.
If you use multiple instances of SQL Downloader and each instance has a separate location to download data from, add several ‘sql’ sections and give each section a unique name (for example, ‘sql_users’ or ‘sql_sales’).
"sql_users": {
"type": "database_1_type",
"options": {
"connection": {
"server": "server_1_address",
"database": "database_1_name",
"username": "user_1_name"
}
}
},
"sql_sales": {
"type": "database_2_type",
"options": {
"connection": {
"server": "server_2_address",
"database": "database_2_name",
"username": "user_2_name"
}
}
}
For each instance of SQL Downloader in the ‘downloaders’ section, add the ‘settings’ parameter and set it to the name of the section that contains settings for this SQL Downloader instance.
"downloaders": {
"sql_downloader_1_id": {
"type": "sql",
"settings": "sql_users",
"entities": ["table_1_name","table_2_name"]
},
"sql_downloader_2_id": {
"type": "sql",
"settings": "sql_usales",
"entities": ["table_1_name","table_2_name"]
}
}
Customize integrators
The ‘integrators’ and ‘ads_storage’ sections define the behavior of integrators.
"integrators": {
"ads_integrator_id": {
"type": "ads_storage"
}
},
"ads_storage": {
"instance_id": "data_warehouse_instance_id",
"username": "dw_email@address.com",
"options": {}
}
If you want to add more parameters or change the defaults, see ADS Integrator.
Schedule Parameters
When scheduling SQL Downloader (see Phases of Building the Data Pipeline -> Production Implementation), provide the parameters from this section in the schedule.
General Parameters
Some parameters must be entered as secure parameters (see Configure Schedule Parameters).
Some parameters contain the names of the nesting parameters, which specifies where they belong in the configuration hierarchy. For example, a parameter entered as sql|options|password is resolved as the following:
"sql": {
"options": {
"password": ""
}
}
Enter such parameters as is (see Schedule Example).
| Name | Typ | Mandatory? | Secure? | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | string | yes | no | n/a | The ID of the SQL Downloader instance being scheduled Must be the same as the 'downloaders -> sql_downloader_id' parameter in the configuration file (see Minimum Layout of the Configuration File) Example: sql_downloader_1 |
| ads_storage|password | string | yes | yes | n/a | The password to access the ADS instance to upload the data to |
| sql|options|connection|password | string | yes | yes | n/a |
|
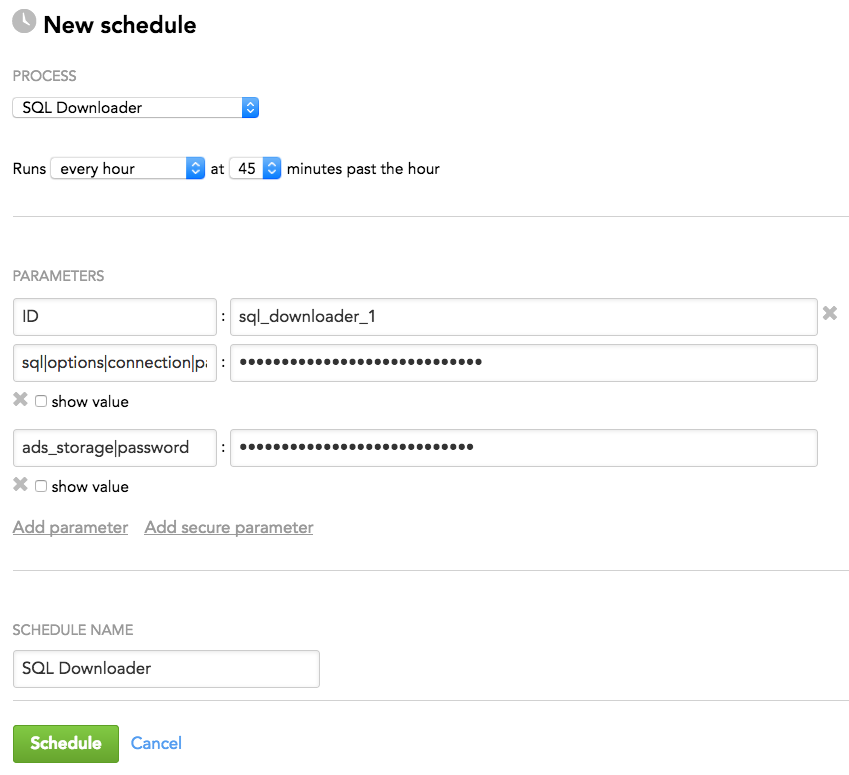
Schedule Example
The following is an example of how you can specify schedule parameters:
Supported Databases
SQL Downloader supports the following databases:
- MySQL Database versions 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0
- PostgreSQL Database versions 12 or older
- All versions of ADS
- MsSQL:
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019
- Microsoft SQL Server 2017
- Microsoft SQL Server 2016
- Microsoft SQL Server 2014
- Microsoft SQL Server 2012
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure SQL Data Warehouse or Parallel Data Warehouse
- Azure SQL Managed Instance (Extended Private Preview)